Efficacy of passive ultrasonic activation and photon-initiated photoacoustic streaming on apical extruded debris of different rotary systems in curved canals
Abstract
Aim: The aim of this study was to investigate the impact of photon-initiated photoacoustic streaming (PIPS) and ultrasonic activator Ultra X (UX) on the extrusion of debris using the One Curve (OC) rotary system and the Reciproc Blue (RB) system in curved canals.
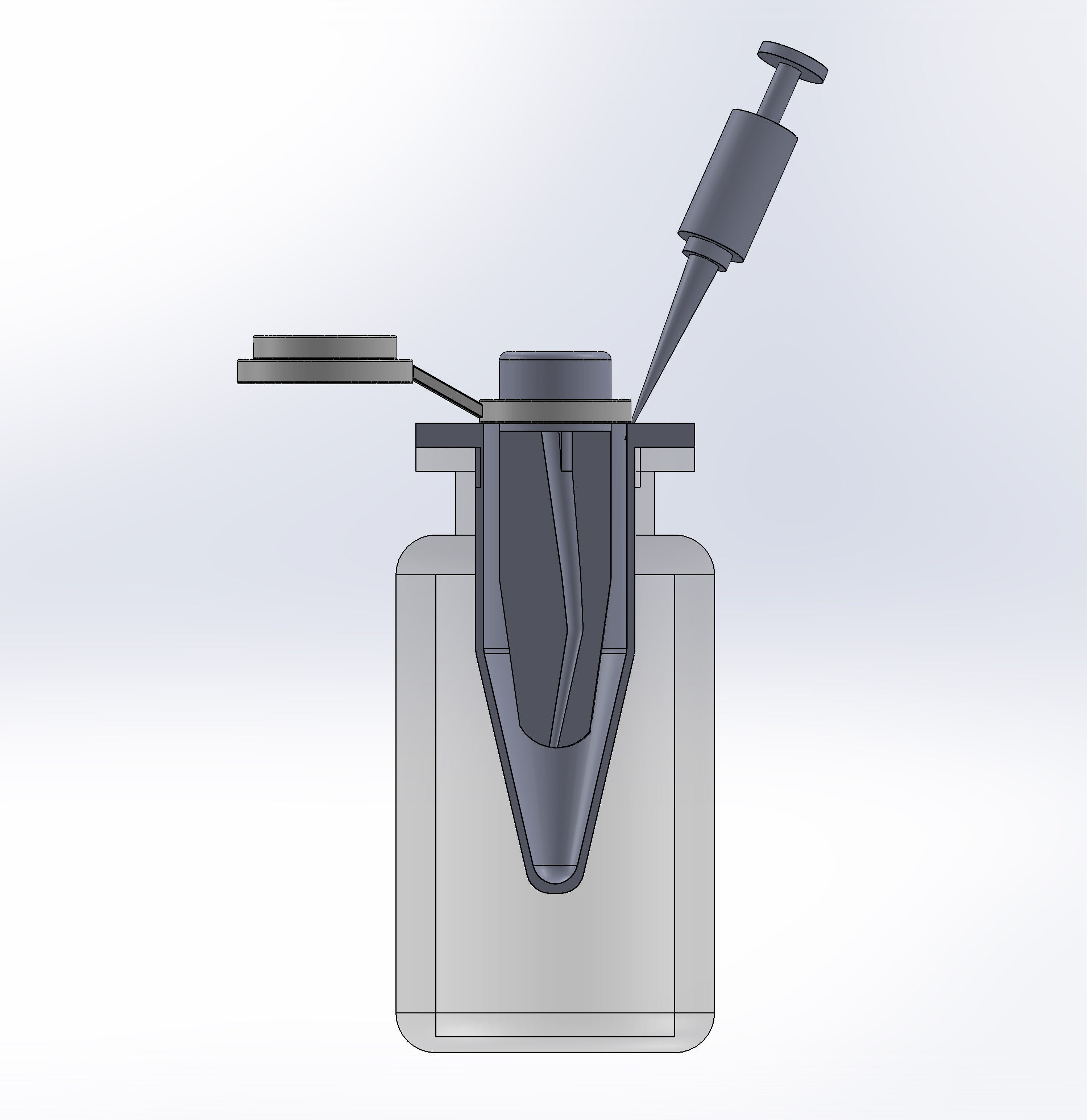
Methodology: Ninety extracted mandibular first molar teeth were divided into six groups (n = 15), Group (1): OC with PIPS, (2) OC with UX, (3) OC with conventional needle irrigation (CNI), (4) RB with PIPS, (5) RB with UX, and (6) RB with CNI. The irrigation activation methods were used in the final irrigation with 2.5 cc of distilled water. The apically protruded debris was collected into pre-weighed Eppendorf tubes. By deducting the tube's initial weight from the final weight, the weight of dry protruded debris was calculated. Two-way ANOVA test was used to analyze the results statistically.
Results: A significant difference was found among all groups (p < 0.05). No statistically significant difference was found among the instrumentation systems, regardless of the irrigation technique employed (p > 0.05). The statistically significant difference was found among the PIPS, UX, and CNI irrigation systems, regardless of the rotary systems (p < 0.05). CNI caused significantly less debris extrusion than the UX ultrasonic irrigation activation systems.
Conclusion: The UX irrigation activation system caused the highest amount of debris extrusion in curved canals. PIPS can be preferred to ultrasonic devices as irrigation activation systems.
How to cite this article:
Akman M, Bozkurt DA, Zogheib C. Efficacy of passive ultrasonic activation and photon-initiated photoacoustic streaming on apical extruded debris of different rotary systems in curved canals. Int Dent Res 2023;13(1):13-18. https://doi.org/10.5577/idr.2023.vol13.no1.3
Linguistic Revision: The English in this manuscript has been checked by at least two professional editors, both native speakers of English.
Full text article
Authors
Copyright © 2023 International Dental Research

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.